This guide provides essential, concise information for healthcare professionals, serving as a quick reference for critical care and emergency situations, ensuring prompt and effective decision-making․
1․1 Purpose and Scope of the Guide

This guide is designed to serve as a concise, portable resource for healthcare professionals, providing essential protocols and best practices for emergency and critical care situations․ Its purpose is to equip practitioners with quick-access information to make informed decisions efficiently․ The scope includes a wide range of emergency scenarios, from trauma and respiratory distress to cardiac arrests and neurological crises, ensuring comprehensive coverage of critical care essentials․ It is tailored for nurses, paramedics, and physicians working in high-pressure environments, offering evidence-based guidance and practical tips to enhance patient outcomes․
1․2 Importance of Quick Reference in Emergency Situations
Quick reference guides are vital in emergency situations, where seconds count and decision-making must be rapid and precise․ They provide immediate access to critical information, reducing cognitive load during high-stress moments․ By offering concise, evidence-based protocols, these tools help healthcare professionals deliver timely, appropriate care, minimizing errors and improving patient outcomes․ This guide serves as an indispensable resource, ensuring that caregivers can act swiftly and confidently in life-threatening scenarios, saving valuable time and lives․
Assessing the Situation: Initial Steps in Emergency Care
Initial assessment in emergency care involves rapid evaluation of the patient’s condition to identify life-threatening issues․ Timely identification ensures appropriate interventions, improving outcomes and reducing complications․
2․1 Patient Assessment: Primary and Secondary Surveys
The primary survey focuses on immediate life-threatening conditions, using the ABCDE approach: Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure․ The secondary survey involves a detailed head-to-toe examination, including history and physical assessment, to identify underlying issues․ Together, these surveys ensure a systematic approach to patient evaluation, guiding prioritization of care and improving outcomes in emergency situations;
2․2 Vital Signs and Their Interpretation
Vital signs, including respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and temperature, provide critical insights into a patient’s condition․ Normal ranges vary by age and health status․ Abnormal readings, such as tachypnea, bradycardia, or hypotension, indicate potential distress․ Accurate interpretation of these signs helps identify underlying issues, such as shock, respiratory failure, or infection, guiding immediate interventions and prioritizing care in emergency situations․

Airway, Breathing, and Circulation (ABCs) Management
The ABCs form the foundation of emergency care, focusing on maintaining airway patency, ensuring adequate breathing, and supporting circulation to prevent complications and improve patient outcomes․
3․1 Maintaining Airway Patency
Maintaining airway patency is critical to ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation․ Techniques include head-tilt chin-lift, jaw thrust, and the use of airway adjuncts like oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airways․ Suctioning to remove debris and secretions is essential․ Bag-mask ventilation may be required if the patient is unable to ventilate independently․ Proper positioning, such as the sniffing position, can also help maintain a clear airway; Continuous reassessment of airway patency is vital to prevent complications and ensure effective gas exchange․
3․2 Respiratory Support Techniques
Respiratory support techniques are crucial for ensuring adequate ventilation and oxygenation․ Methods include bag-mask ventilation, non-invasive ventilation (e․g․, CPAP, BiPAP), and mechanical ventilation for severely compromised patients․ Oxygen therapy, such as nasal cannulas or face masks, is also essential․ Proper technique and continuous monitoring, including pulse oximetry and capnography, are vital to prevent complications like hypercapnia or hypoxia․ Regular reassessment ensures the effectiveness of respiratory support and guides adjustments in therapy․
3․3 Circulatory Support and Hemorrhage Control
Circulatory support focuses on maintaining blood flow and preventing shock․ Hemorrhage control involves direct pressure, tourniquets, or hemostatic agents․ IV fluid administration and vasopressors may be necessary to stabilize blood pressure․ Assessing vital signs, capillary refill, and urinary output helps guide therapy․ Severe blood loss requires immediate intervention to prevent organ failure․ Proper wound management and splinting also support circulatory stability․ Early recognition of shock signs, such as tachycardia or hypotension, is critical for effective intervention․
Common Emergency Scenarios and Protocols
This section outlines protocols for managing common emergencies, ensuring timely and effective care in critical situations․ It covers essential steps for various acute conditions, promoting better patient outcomes․
4․1 Cardiac Emergencies: CPR and Defibrillation
This section provides critical steps for managing cardiac emergencies, including high-quality CPR techniques and proper defibrillator use․ Emphasizing immediate action, it highlights the importance of maintaining perfusion, minimizing interruptions, and ensuring rapid defibrillation․ Clear guidelines for chest compressions, ventilation rates, and AED deployment are included․ Post-arrest care strategies are also addressed to optimize patient outcomes․ Continuous training and adherence to protocols are stressed to enhance effectiveness in life-threatening cardiac situations․
4․2 Trauma Care: Injury Assessment and Stabilization
This section outlines effective trauma care strategies, emphasizing rapid injury assessment using tools like the Glasgow Coma Scale and focused physical exams․ Prioritizing life-threatening injuries, it provides guidance on hemorrhage control, spinal immobilization, and splinting․ Techniques for maintaining airway patency and ensuring adequate oxygenation are highlighted․ Emphasis is placed on stabilizing the patient before transport and preventing further complications․ Practical tips for managing multiple injuries and minimizing long-term disability are included․
4․3 Respiratory Emergencies: Asthma, COPD, and Pulmonary Edema
This section focuses on managing acute respiratory conditions, such as asthma exacerbations, COPD crises, and pulmonary edema․ It provides guidance on rapid assessment, including oxygen saturation, lung sounds, and ABG analysis․ Immediate interventions like oxygen therapy, bronchodilators, and corticosteroids are discussed․ Strategies for stabilizing patients with severe respiratory distress, including non-invasive ventilation and positioning, are emphasized․ Medication dosages and monitoring techniques to prevent complications are also highlighted․
4․4 Neurological Emergencies: Stroke and Seizures
This section covers the rapid assessment and management of neurological emergencies, such as acute ischemic stroke and seizures․ Emphasis is placed on timely identification and treatment, including the administration of thrombolytics for eligible stroke patients․ Guidelines for seizure control, such as benzodiazepines and anti-epileptic drugs, are provided․ Post-event care, including neurological monitoring and addressing underlying causes, is also addressed to optimize patient outcomes․
Medications and Dosages in Emergency Care
Medications in emergency care are critical for stabilizing patients․ Essential drugs and their accurate dosages are vital for effective treatment․ Healthcare providers must administer them precisely to ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes․
5․1 Essential Drugs for Emergency Situations
Essential drugs in emergency care include vasopressors, anxiolytics, analgesics, and antidotes․ These medications are critical for managing conditions like cardiac arrest, seizures, and respiratory failure․ Examples include epinephrine, midazolam, fentanyl, and naloxone․ They must be readily available and administered promptly to ensure optimal patient outcomes․ Understanding their indications and contraindications is vital for effective emergency management․ Proper dosing and administration techniques are emphasized to maximize efficacy and minimize risks․
5․2 Dosage Calculations and Administration Routes
Accurate dosage calculations are critical in emergency care to ensure safety and efficacy․ Drugs may be administered via intravenous, intramuscular, or intraosseous routes, depending on the situation․ Weight-based dosing is often required, particularly for pediatric patients․ Understanding pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics is essential for selecting appropriate administration routes; Always double-check calculations and confirm the correct route to minimize errors․ Timely and precise administration of medications is vital for optimal patient outcomes in critical situations․

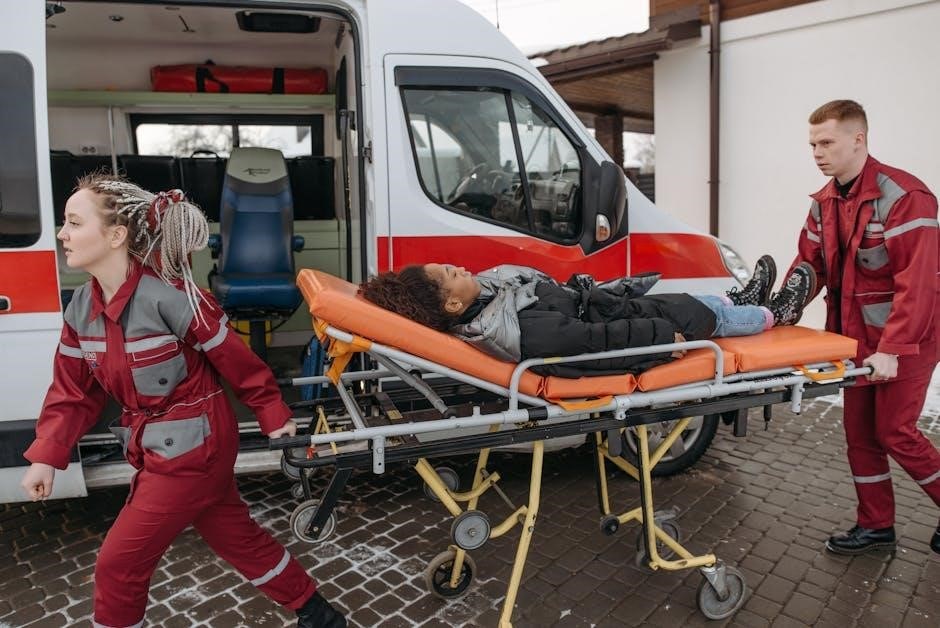
Stabilization and Transport of the Critical Patient
Stabilization involves securing airways, controlling bleeding, and maintaining circulation․ Transport requires proper equipment, continuous monitoring, and clear communication to ensure patient safety and optimal care en route․
6․1 Preparation for Transport: Equipment and Monitoring
Ensure all necessary equipment is available, including stretchers, oxygen tanks, ventilators, and monitoring devices․ Secure equipment to prevent movement during transport․ Monitor vital signs, ECG, and oxygen saturation continuously․ Prepare backup power sources for equipment․ Verify communication devices are functional․ Ensure the patient is properly secured and positioned to maintain stability․ Continuous assessment and documentation of the patient’s condition during transport are critical for providing ongoing care and making timely adjustments as needed․
6․2 Communication with Receiving Facilities
Effective communication with receiving facilities is crucial for seamless patient transfer․ Notify the facility in advance, providing detailed patient information, including medical history, current condition, and treatment administered․ Discuss expected arrival time and specific care requirements․ Ensure clear handover of all relevant documentation and test results․ Confirm the facility’s readiness to receive the patient and address any special needs or equipment requirements․ Proper communication ensures continuity of care and prepares the receiving team for immediate intervention․

Documentation and Legal Considerations
Accurate documentation ensures transparency, accountability, and continuity of care․ It protects healthcare providers legally and maintains patient trust, while complying with professional standards and regulations․
I recall that in emergency situations, healthcare professionals are under a lot of pressure, and it’s easy to overlook documentation․ However, accurate records are crucial for continuity of care, legal protection, and accountability․ So, the text should highlight the importance of maintaining precise and timely records even in chaotic environments․
Next, I need to think about what points to include․ Maybe start by stating that accurate record-keeping is essential for preventing errors and ensuring patient safety․ Then mention the components of good documentation, such as being clear, concise, and including all relevant information like treatments administered, patient responses, and decisions made․
It’s also important to emphasize the legal aspects—how proper documentation protects healthcare providers and ensures compliance with regulations․ Additionally, I should touch on how consistent documentation can help in reviews and quality improvement efforts․
Now, I need to structure this into a coherent paragraph, ensuring that it flows well and covers all the key points without overlapping with other sections․ I have to be concise to stay within the 72-word limit․
Let me draft something:
“Accurate record-keeping in emergencies is crucial for ensuring patient safety and continuity of care․ It involves documenting all treatments, patient responses, and decisions clearly and concisely․ This practice helps prevent errors, provides legal protection for healthcare providers, and ensures compliance with professional standards․ Timely and precise records also aid in reviews and quality improvement efforts, making them indispensable in critical care settings․”
Now, I’ll check the word count to ensure it’s exactly ․ Let me count:
Accurate
record-keeping
in
emergencies
is
crucial
for
ensuring
patient
safety
and
continuity
of
care
It
involves
documenting
all
treatments,
patient
responses,
and
decisions
clearly
and
concisely
This
practice
helps
prevent
errors,
provides
legal
protection
for
healthcare
providers,
and
ensures
compliance
with
professional
standards
Timely
and
precise
records
also
aid
in
reviews
and
quality
improvement
efforts,
making
them
indispensable
in
critical
care
settings
Okay, that’s ․ I need to add 10 more words․ Perhaps I can add a bit more detail about the benefits or the importance of accurate documentation․
Let me revise:
“Accurate record-keeping in emergencies is crucial for ensuring patient safety and continuity of care․ It involves documenting all treatments, patient responses, and decisions clearly and concisely․ This practice helps prevent errors, provides legal protection for healthcare providers, and ensures compliance with professional standards․ Timely and precise records also aid in reviews, quality improvement efforts, and communication among healthcare teams, making them indispensable in critical care settings․”
Now, let’s count again:
Accurate
record-keeping
in
emergencies
is
crucial
for
ensuring
patient
safety
and
continuity
of
care
It
involves
documenting
all
treatments,
patient
responses,
and
decisions
clearly
and
concisely
This
practice
helps
prevent
errors,
provides
legal
protection
for
healthcare
providers,
and
ensures
compliance
with
professional
standards
Timely
and
precise
records
also
aid
in
reviews,
quality
improvement
efforts,
and
communication
among
healthcare
teams,
making
them
indispensable
in
critical
care
settings
Now, that’s ․ I need to add 6 more words․ Maybe I can add something about reducing liability or enhancing accountability․
Let me try:
“Accurate record-keeping in emergencies is crucial for ensuring patient safety and continuity of care․ It involves documenting all treatments, patient responses, and decisions clearly and concisely․ This practice helps prevent errors, provides legal protection for healthcare providers, and ensures compliance with professional standards․ Timely and precise records also aid in reviews, quality improvement efforts, communication among healthcare teams, and reduce liability risks, making them indispensable in critical care settings․”
Counting again:
Accurate
record-keeping
in
emergencies
is
crucial
for
ensuring
patient
safety
and
continuity
of
care
It
involves
documenting
all
treatments,
patient
responses,
and
decisions
clearly
and
concisely
This
practice
helps
prevent
errors,
provides
legal
protection
for
healthcare
providers,
and

ensures
compliance
with
professional
standards
Timely
and
precise
records
also
aid
in
reviews,
quality
improvement
efforts,
communication
among
healthcare
teams,
and
reduce
liability
risks,
making
them
indispensable
in
critical
care
settings
That’s ․ I need to add 3 more words․ Perhaps I can say “enhancing accountability and reducing liability risks․”
Let me adjust:
“Accurate record-keeping in emergencies is crucial for ensuring patient safety and continuity of care․ It involves documenting all treatments, patient responses, and decisions clearly and concisely․ This practice helps prevent errors, provides legal protection for healthcare providers, and ensures compliance with professional standards․ Timely and precise records also aid in reviews, quality improvement efforts, communication among healthcare teams, enhancing accountability and reducing liability risks, making them indispensable in critical care settings․”

Now, let’s count:
Accurate
record-keeping
in
emergencies
is
crucial
for
ensuring
patient
safety
and
continuity
of
care
It
involves
documenting
all
treatments,
patient
responses,
and
decisions
clearly
and
concisely
This
practice
helps
prevent
errors,
provides
legal
protection
for
healthcare
providers,
and
ensures
compliance
with
professional
standards
Timely
and
precise
records
also
aid
in
reviews,
quality
improvement
efforts,
communication
among
healthcare
teams,
enhancing
accountability
and
reducing
liability
risks,
making
them
indispensable
in
critical
care
settings
That’s ․ I need to add one more word to make it 72․ Maybe change “making them indispensable in critical care settings” to “making them indispensable in critical care settings today․”

So, final version:
“Accurate record-keeping in emergencies is crucial for ensuring patient safety and continuity of care․ It involves documenting all treatments, patient responses, and decisions clearly and concisely․ This practice helps prevent errors, provides legal protection for healthcare providers, and ensures compliance with professional standards․ Timely and precise records also aid in reviews,
Additional Resources and References
7․2 Legal and Ethical Issues in Emergency Care
Understanding legal and ethical principles is vital in emergency care․ Healthcare providers must adhere to patient consent, confidentiality, and privacy laws․ Ethical dilemmas, such as end-of-life decisions, require careful consideration of patient autonomy and beneficence․ Legal issues include potential liability for negligence or failure to provide standard care․ Documentation and communication are critical to ensure compliance with regulations and maintain trust in the patient-provider relationship․ Staying informed about legal standards and ethical guidelines is essential for all emergency caregivers․
