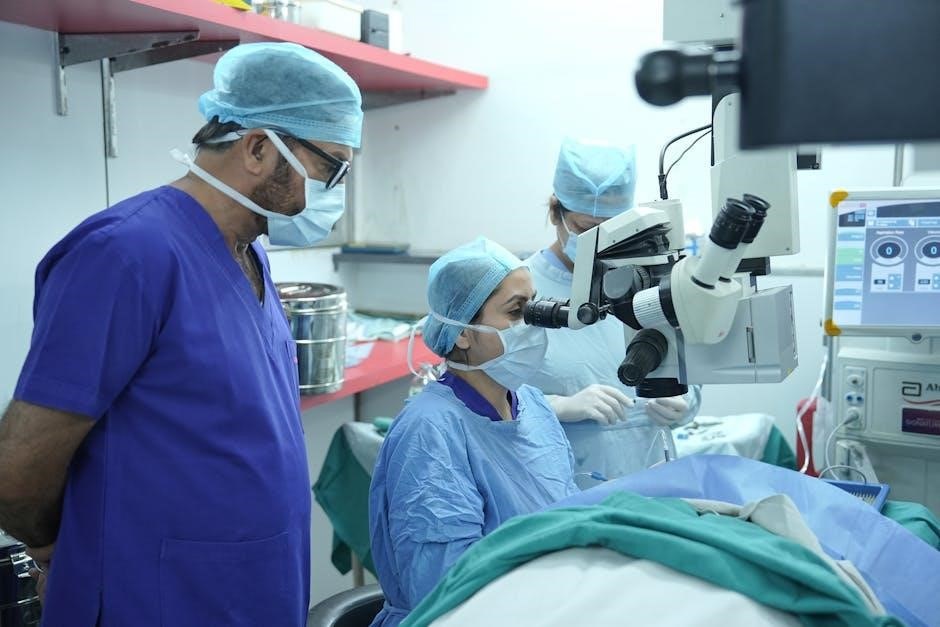
Cataract surgery involves replacing a clouded lens with an intraocular lens (IOL), improving vision. Laser-assisted surgery uses femtosecond lasers for precise cuts, while manual surgery employs phacoemulsification. Both methods aim for clear vision, with laser offering enhanced precision and manual being cost-effective and widely used.
Overview of Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery is a medical procedure to restore vision by removing a clouded lens and replacing it with an intraocular lens (IOL). It is a common and highly effective treatment for cataracts, a condition that impairs vision due to lens opacity. The surgery can be performed using traditional manual techniques, such as phacoemulsification, or advanced laser-assisted methods. Both approaches aim to achieve clear vision, but they differ in technique, precision, and recovery time. The choice between laser and manual surgery depends on various factors, including the patient’s eye condition, surgeon preference, and cost considerations. Both methods are safe and effective when performed by experienced surgeons.
Key Differences Between Laser and Manual Cataract Surgery
Laser-assisted cataract surgery uses femtosecond laser technology for precise incisions and capsulotomy, offering enhanced accuracy. Manual surgery relies on phacoemulsification, a traditional method requiring surgical skill. Laser surgery is generally more expensive but provides superior precision, especially in complex cases. Recovery times are comparable, though laser may reduce complications. Both methods are effective, with outcomes depending on the surgeon’s expertise. Patient preferences, cost, and specific eye conditions influence the choice between these two approaches.
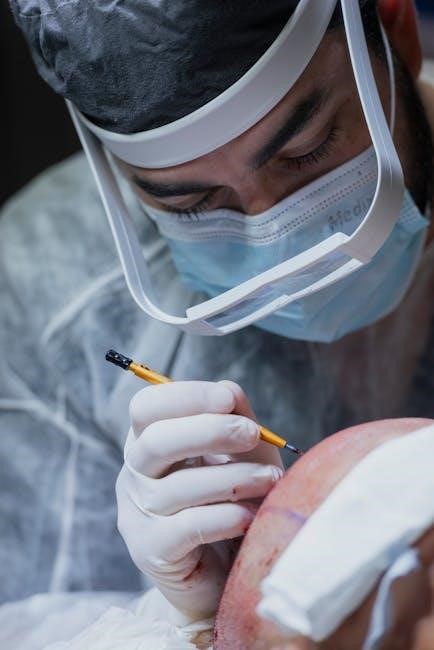
Traditional Manual Cataract Surgery
Manual cataract surgery, or phacoemulsification, uses ultrasonic waves to break and remove the cloudy lens. It is a reliable, cost-effective method without requiring advanced laser technology.
Procedure and Techniques

Manual cataract surgery involves making small incisions in the cornea to access the cloudy lens. Using ultrasonic waves, the lens is emulsified and suctioned out. A foldable intraocular lens (IOL) is then inserted through the incision. The procedure relies on the surgeon’s skill to manually create a circular opening in the lens capsule and remove the cataract. This technique is highly effective and widely used, offering a reliable method for restoring vision. The process is typically quick, with most surgeries completed in under 30 minutes, making it a trusted approach for cataract treatment.
Advantages of Manual Phacoemulsification
Manual phacoemulsification is a cost-effective and widely accessible method for cataract removal. It does not require specialized laser equipment, making it more readily available in various healthcare settings. The procedure is highly effective in experienced hands, offering precise control for surgeons during lens emulsification and removal. It is particularly advantageous in cases where laser technology is unavailable or unsuitable. Additionally, manual techniques allow for flexibility in handling complex cataracts and reduce reliance on advanced technology. This approach has a long-standing track record of success, ensuring clear vision outcomes for patients worldwide, making it a reliable choice for cataract treatment.

Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery
Laser-assisted cataract surgery uses femtosecond laser technology for precise incisions and lens fragmentation, enhancing accuracy and consistency in achieving improved vision outcomes for patients.

Role of Femtosecond Laser Technology
Femtosecond laser technology plays a critical role in laser-assisted cataract surgery by enabling precise corneal incisions, capsulorhexis, and lens fragmentation. The laser’s high accuracy reduces reliance on manual techniques, minimizing complications. It creates consistent, reproducible results, particularly in complex cases, and enhances surgical safety. The femtosecond laser is also used to soften the cataract, making removal easier. This technology improves the overall precision of the procedure, leading to better visual outcomes and faster healing. Its advanced capabilities make it a valuable tool in modern cataract surgery, offering patients a more predictable and refined experience.
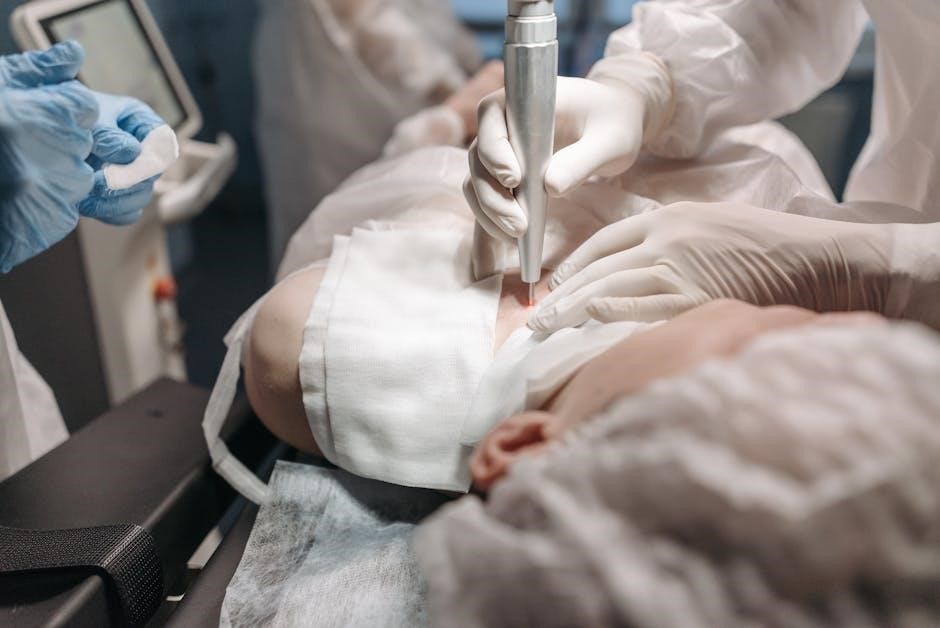
Benefits of Laser-Assisted Surgery
Laser-assisted cataract surgery offers enhanced precision, particularly in creating corneal incisions and capsulorhexis. The femtosecond laser ensures consistent and reproducible results, reducing human error. It minimizes complications like cystoid macular edema and improves wound sealing, promoting faster healing. Additionally, laser technology facilitates customized incisions based on individual eye anatomy, optimizing intraocular lens placement. Patients often experience reduced recovery time and improved visual clarity post-surgery. While outcomes may not differ significantly from manual surgery, the laser’s precision provides added confidence for both surgeons and patients, making it a preferred choice for complex cases or specific patient needs.
Comparison of Outcomes and Recovery
Both laser and manual cataract surgeries yield similar visual outcomes, but laser-assisted surgery may offer faster recovery due to precise incisions, reducing healing time for some patients.
Precision and Accuracy
Laser-assisted cataract surgery offers enhanced precision due to femtosecond laser technology, enabling consistent corneal incisions and capsular openings. This reduces human error compared to manual surgery, where precision depends on the surgeon’s skill. The laser’s ability to create precise, reproducible cuts minimizes variability, potentially improving surgical outcomes. However, studies show no significant difference in visual results between the two methods. Manual phacoemulsification remains highly effective, with experienced surgeons achieving excellent accuracy. Ultimately, the choice between laser and manual surgery may depend on individual patient needs and the surgeon’s expertise, as both methods prioritize precision to ensure optimal vision correction and healing.
Recovery Time and Patient Experience
Recovery time for both laser-assisted and manual cataract surgery is generally short, with most patients resuming normal activities within days. Laser surgery often minimizes trauma to the eye, potentially reducing discomfort and irritation post-operatively. Patients may experience less dryness or eye strain with laser-assisted procedures. However, studies show no significant difference in long-term recovery outcomes between the two methods. Both techniques aim to provide a smooth and comfortable recovery, with patients typically achieving improved vision within a few days. The overall patient experience is positive for both approaches, with vision clarity and reduced dependency on glasses being common benefits.
Cost and Accessibility
Laser-assisted cataract surgery is typically more expensive due to the advanced technology used. Manual surgery remains more cost-effective and widely accessible, with comparable outcomes for many patients.
Cost Differences Between Laser and Manual Surgery
Laser-assisted cataract surgery is generally more expensive due to the advanced femtosecond laser technology used. The cost includes the laser’s precision in creating incisions and fragmenting the lens. Manual surgery, or phacoemulsification, is more cost-effective and widely covered by insurance. Laser surgery may incur additional out-of-pocket expenses, as some insurances do not cover the extra fees for laser technology. While laser offers enhanced precision, the higher cost may not always justify the investment for patients with straightforward cataracts. Surgeons’ fees and facility charges for laser surgery also contribute to the price difference, making manual surgery a more accessible option for many patients.
Complications and Safety
Both laser and manual cataract surgeries are safe, with low complication rates. Laser-assisted surgery reduces infection risks, while manual techniques may carry higher inflammation risks post-operation.
Risks Associated with Each Method
Both laser and manual cataract surgeries carry risks, though overall complication rates are low. Laser-assisted surgery may pose risks like laser-related complications or incomplete capsulotomies. Manual surgery risks include infection, inflammation, or capsular rupture; Post-operative issues such as intraocular lens (IOL) misplacement or retinal detachment can occur in either method. Laser surgery may reduce certain risks like human error during incisions, but it is not risk-free. Patient-specific factors, such as eye health and surgeon expertise, influence safety outcomes. Both methods are considered safe, but the choice depends on individual conditions and surgical preferences.

Both laser and manual cataract surgeries offer effective vision restoration. Patients should weigh factors like cost, precision, and personal preferences when choosing a method, ensuring informed decisions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Method
When deciding between laser and manual cataract surgery, patients should consider cost, precision, recovery time, and personal preferences. Laser surgery offers enhanced accuracy and faster healing but is more expensive. Manual surgery is cost-effective and widely used, with proven effectiveness. Surgeon expertise and the complexity of the cataract also play a role. Patients should discuss their lifestyle, budget, and medical needs with their doctor to make an informed decision. Ultimately, both methods aim to restore vision, but individual circumstances will guide the best choice.